O-DU High Overview¶
O-DU High Architecture¶
O-DU implements the functional blocks of L2 layer of a 5G NR protocol stack in SA(StandAlone) mode. These layers primarily include NR MAC, NR Scheduler and NR RLC layers.
O-DU modules are developed as shown in the below diagram.
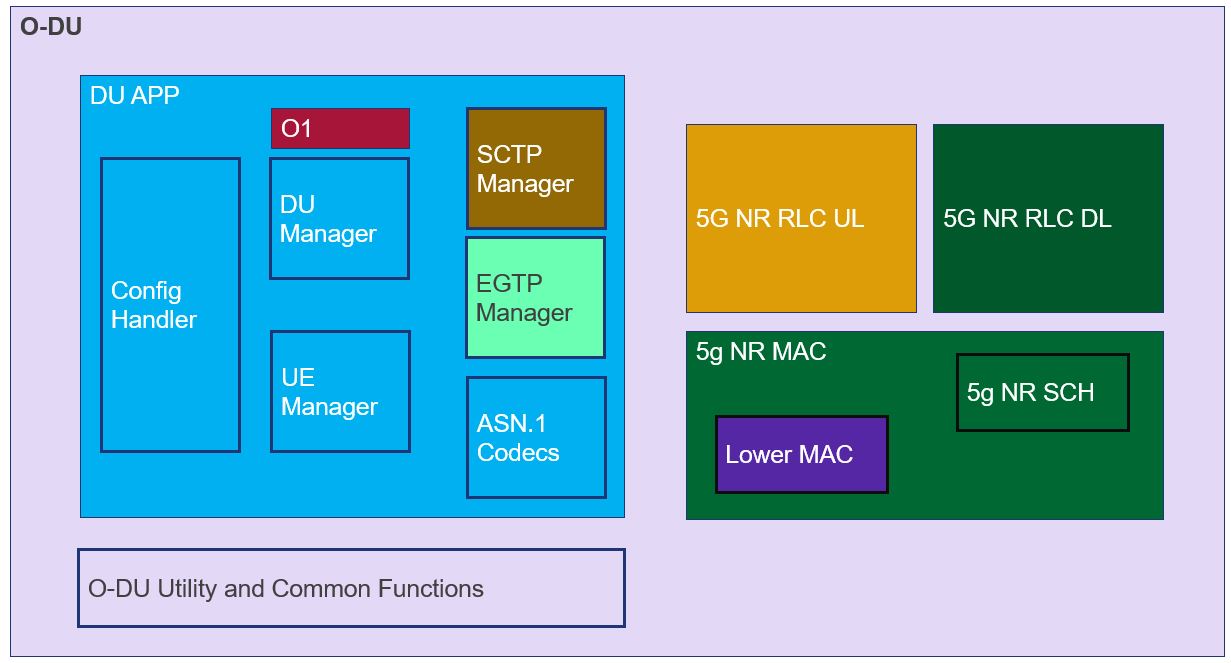
Figure 1 - O-DU High Architecture Diagram¶
O-DU High Thread Architecture¶
As shown in Figure 1, there are multiple entities within O-DU High. Modules sharing a given color belong to one thread. O-DU architecture can be defined at a thread level as follows:
Thread 1: O-DU thread
Thread 2: DU APP inclusive of Config Handler, DU Manager, UE Manager, and ASN.1 Codecs
Thread 3: 5G NR RLC DL and MAC (inclusive of 5G NR SCH and Lower MAC)
Thread 4: 5G NR RLC UL
Thread 5: SCTP Handler
Thread 6: Lower MAC Handler
Thread 7: EGTP Handler
Thread 8: O1
O-DU High Modules¶
DU APP¶
This module configures and manages all the operations of O-DU. It interfaces with external entities as follows:
OAM: DU APP interacts with OAM on the O1 interface for configuration, alarms and performance management.
O-CU: DU APP interacts with O-CU for RAN functionalities over the F1 interface which is built on SCTP. Control messages are exchanged on the F1-C interface and data messages on the F1-U interface.
RIC: DU APP interacts with RIC on E2 interface over SCTP.
DU App submodules are as follows:
Config Handler manages the configurations received on O1 interfaces and stores them within DU APP context.
DU Manager handles all cell operations at the DU APP.
UE Manager handles UE contexts at the DU APP.
SCTP handler is responsible for establishing SCTP connections with O-CU, RIC on the F1AP and E2AP interfaces respectively.
EGTP handler is responsible for establishing EGTP connection with O-CU for data message exchange on the F1-U interface.
ASN.1 Codecs contain ASN.1 encode/decode functions which are used for System information, F1AP and E2AP messages.
5G NR RLC¶
This module provides services for transferring the control and data messages between MAC layer and O-CU (via DU App).
5G NR RLC UL and 5G NR RLC DL are the sub modules of this module that implement uplink and downlink functionality respectively.
5G NR MAC¶
This module uses the services of the NR physical layer to send and receive data on the various logical channels. Functions of the 5G NR MAC module are as follows:
5G NR MAC is responsible for multiplexing and de-multiplexing of the data on various logical channels.
5G NR SCH schedules resources in UL and DL for cell and UE based procedures. 5G NR SCH is completely encapsulated within the 5G NR MAC i.e., all interactions of the 5G NR SCH is via the 5G NR MAC.
Lower MAC interfaces between the MAC and the O-DU Low. It implements all the messages of FAPI specification. It has a receiver thread to handle messages from L1.
O-DU Utility and Common Functions¶
These modules contain platform specific files and support O-DU High functionality and message exchanges.
O1 Module¶
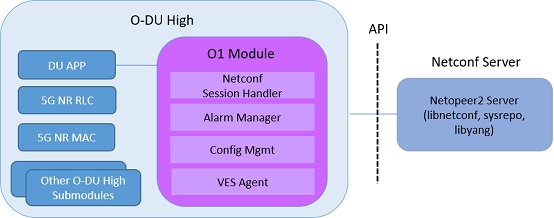
Figure 2 - O1 Architecture¶
As shown in figure 2 the O1 module runs as a thread in O-DU High. Alarm communication happens over a Unix socket between the O1 and O-DU threads. O1 module uses API calls for interacting with the Netconf server(Netopeer) and datastore(sysrepo) for providing the Netconf interface.
O1 architecture has following components:
Netconf Session Handler: Subscribe to Netconf YANG modules and events. Register callback handler methods.
VES Agent : Sends the VES events to SMO
Alarm Manager: Stores and manages(add/updated/delete) alarms.
Alarm Interface : Provides an interface to O-DU High threads for sending the alarm messages to O1 module over Unix socket.
Config Interface : Interface to handle the configurations sent from SMO to the stack
Netopeer server: Serves the northbound SMO/OAM Netconf requests.
O-DU-High Interfaces¶
This section describes the other modules that O-DU High interfaces with, as shown in below diagram.
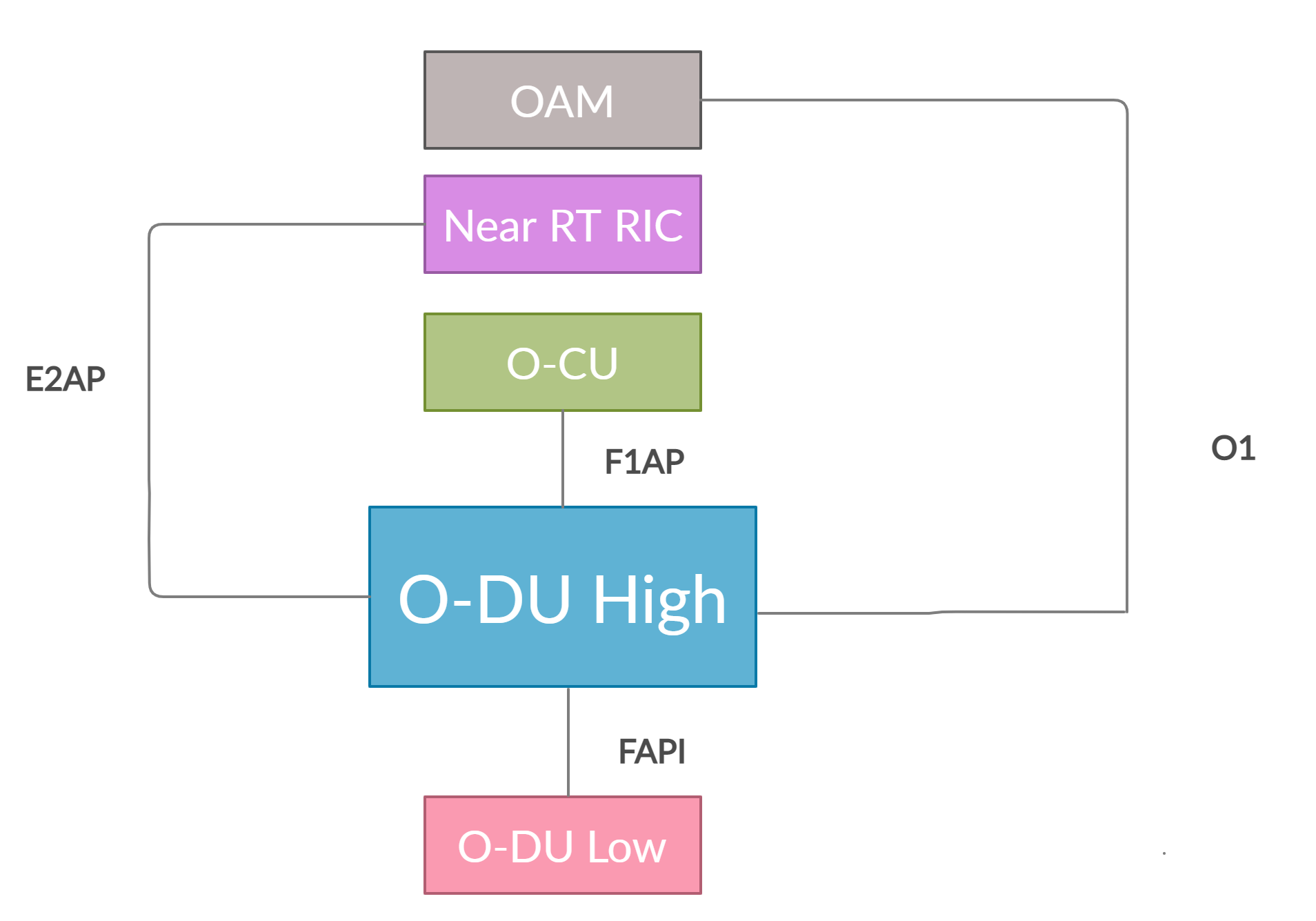
Figure 3 - O-DU High Interfaces¶
As shown in Figure 3, O-DU High interfaces with the following modules:
O-CU: O-DU High communicates with O-CU on the F1AP interface. The control message exchanges are on F1-C while data message exchanges are on F1-U interfaces. The below F1AP messages on F1-C are implemented, as per 3GPP 38.473-f60 v15.3:
Interface Management
F1 Setup
gNB-DU Configuration Update
F1 Reset
UE Context Management
UE Context Setup
UE Context Modification
UE Context Release
RRC Message Transfer
Initial UL RRC Message Transfer
DL RRC Message Transfer
UL RRC Message Transfer
RRC Delivery Report
Near RT RIC: O-DU High communicates with Near RT RIC on the E2 interface. The below E2AP messages are implemented, as per ORAN WG3.E2AP v01.00:
Global Procedures
E2 Setup
Near RT RIC Functional Procedures
RIC Subscription
RIC Indication
O-DU Low: O-DU High communicates with O-DU Low on the FAPI interface. The below FAPI messages are supported, as per FAPI interface files shared by Intel:
P5 messages - PHY mode control interface
PARAM.request/PARAM.response
CONFIG.request/CONFIG.response
START.request
STOP.request
STOP.indication
P7 messages - Main data path interface
DL_TTI.request
UL_TTI.request
SLOT.indication
UL_DCI.request
TX_Data.request
RX_Data.indication
CRC.indication
UCI.indication
RACH.indication
OAM: O-DU High communicates with OAM on the O1 interface.
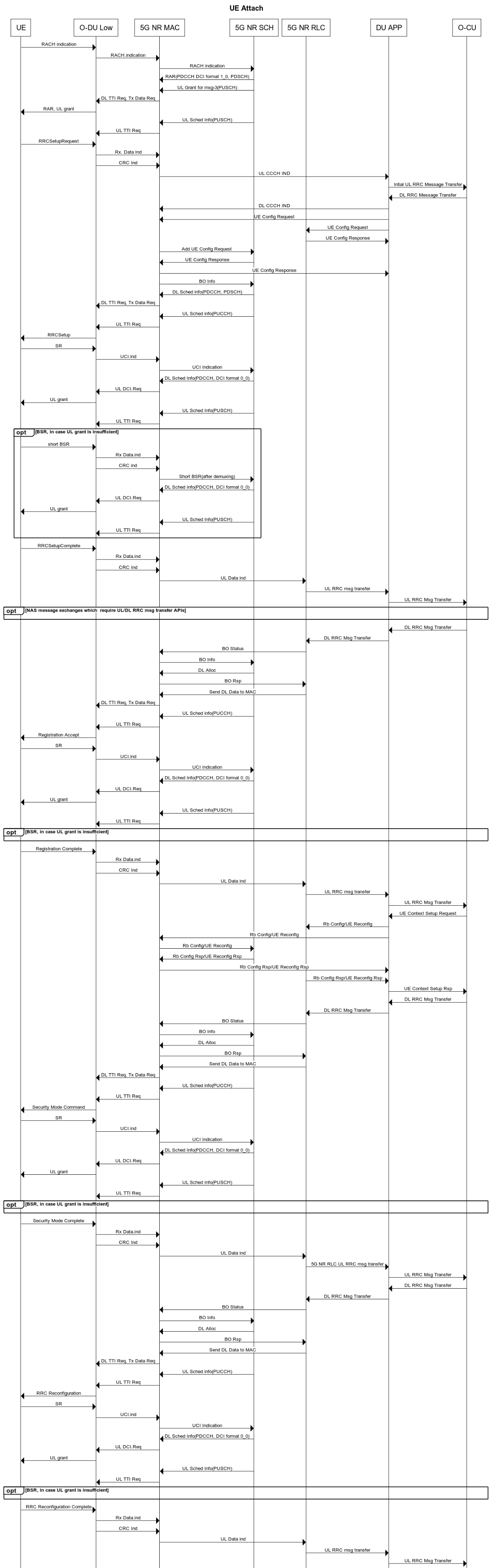
O-DU High functionality¶
Cell Up and Broadcast Procedure¶
This section describes the cell-up procedure within O-DU High.
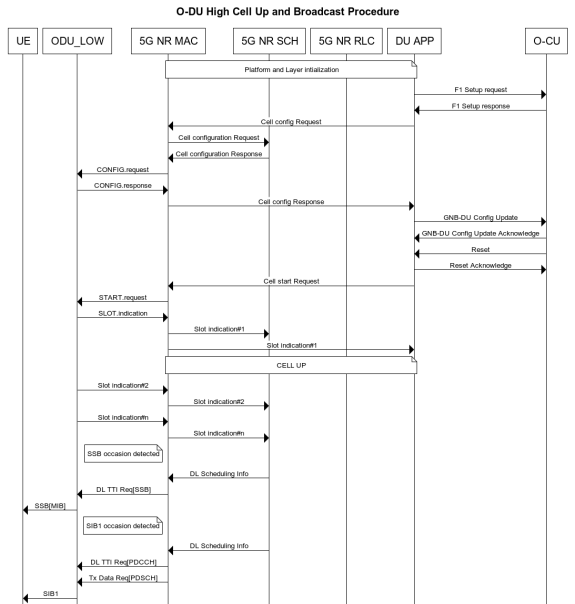
Figure 4 - O-DU High Cell Up and Broadcast Procedure¶
As seen in the Figure 4, - The DU APP module of O-DU High sends F1 Setup Request to O-CU. This message contains a list of cells that the O-DU High has been configured with.
The O-CU responds with F1 Setup Response. This message contains a list of cells which must be activated.
The O-DU High scans the list of cells received and sends corresponding cell configurations to 5G NR MAC.
5G NR MAC, in-turn configures the 5G NR SCH. It also configures the O-DU Low via the Lower MAC module.
On receiving the cell config response, DU APP sends a gNB DU Config Update towards the O-CU. The O-CU responds with gNB DU Config Update ACK towards the O-DU High.
The DU APP now exchanges F1 Reset message with the O-CU to initialize the UE contexts.
DU APP sends Cell Start Req towards 5G NR MAC. This message is translated by the Lower MAC into the FAPI message START.request towards the O-DU Low.
On receiving START.request, O-DU Low begins to send slot indications towards 5G NR MAC via the lower MAC. The frequency of these slot indications is determined by the numerology(Mu) supported. 5G NR MAC forwards these slot indications to the 5G NR SCH and DU APP modules.
When the first slot indication reaches the DU APP, cell is marked as up.
The 5G NR SCH, keeps tracking the SSB and SIB1 ocassions on receiving regular slot indications. On detecting the relevant ocassion, 5G NR SCH schedules SSB/SIB1 and forwards the DL Scheduling Information to 5G NR MAC.
The 5G NR MAC mutiplexes the PDU and sends SSB/SIB1 packets towards the O-DU Low through the Lower MAC.
Closed Loop Automation Procedure¶
This section describes the closed loop automation procedure within O-DU High.
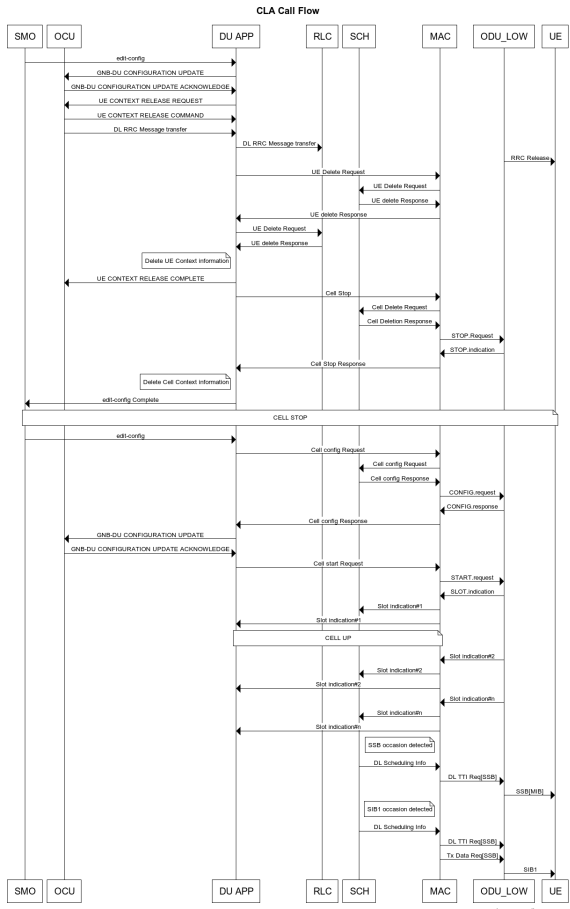
Figure 6 - O-DU High Closed Loop Automation Procedure¶
SMO commands ODU-High to bring the cell down via O1 interface.
DU-APP module of ODU-High sends GNB-DU configuration update message to O-CU. It contains the details of cell to be deleted. O-CU acknowledges this message by sending GNB-DU configuration update acknowledgment.
For each UE, DU APP sends UE Context Release Request to O-CU with information about the to be released. O-CU responds with UE Context Release request. It contains the RRC release message. O-DU high sends this RRC Release message to UE.
DU APP then sends UE delete request to MAC and RLC. Once a confirmation is received from both MAC and RLC, DU APP deletes UE from its own database as well.
Once all UEs are released, O-DU High sends STOP.Request to L1. L1 responds with stop indication.
Once cell has stopped, DU APP sends cell delete request to MAC. On receiving confimation from MAC, DU APP deletes cell information from its own database as well and sends UE Context Release Complete.
On receiving cell bring up command from SMO, the complete Cell bring up and UE attach procedure will be repeated (as explained in above sections)
O1 Netconf get-alarm list procedure¶
This section describes the Health Status Retrieval scenario of O-DU High health-check. It enables a northbound client(SMO) to retrieve the health of the O-DU High based on the last self-check performed. The alarm-list is provided as the response to the request via O1 Netconf interface.
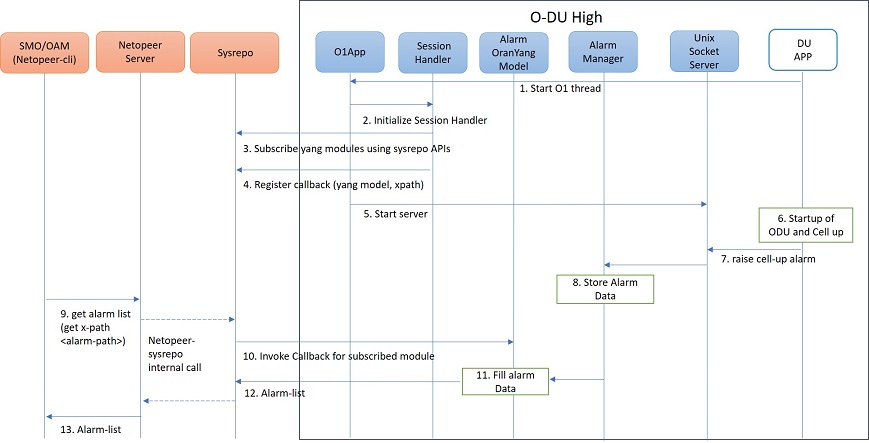
Figure 7 - O1 get alarm-list flow¶
As seen in the Figure 7,
On the cell state change from de-active to activate, DU APP module raises a cell up alarm message and sends it over the Unix socket using the Alarm Interface API.
On other side a Unix socket server, running as a thread, in O1 module receives the cell up alarm message and it passes on the alarm information to the Alarm Manager.
Alarm Manager stores the alarm data in a list.
Whenever SMO/OAM requires the current alarm list, it sends a Netconf get request. The request is received by the Netopeer Server and a callback method, registered with the Session Handler, is invoked.
The callback function fetches the alarm list from Alarm Manager and sends it back to the client (SMO/OAM) via Netconf interface.
OSC Testcases Supported¶
The O-DU High partially supports below use-cases:
Traffic Steering
Health Check